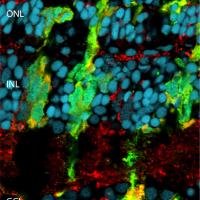
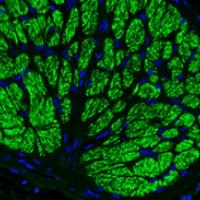
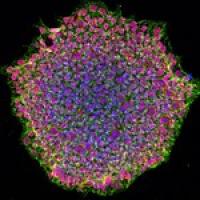
939 items


NEI Press Office
We can connect media professionals with the latest vision research info. Get in touch!
Email: neinews@nei.nih.gov
Phone: 301-496-5248